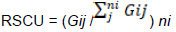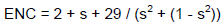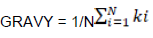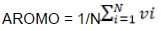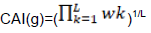Analysis of factors affecting codon usage bias in human papillomavirus


Опубликована Янв. 31, 2018
Последнее обновление статьи Авг. 23, 2022
Abstract
Indices of codon usage pattern of human papillomavirus (HPV) were analyzed to understand the key determinants of synonymous codon usage in the HPV genome. The complete sequences of 39 HPV genomes were downloaded from the website of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. The relative synonymous codon usage values, effective number of codons, GC content, percentage of GCs at the third position of synonymous codons (GC3s), codon adaptation index, hydrophobicity, aromaticity of conceptually translated gene products were calculated using the Codon W 1.4.2 program. HPV preferentially used codons ending with A/U. By comparing relative synonymous codon usage of the HPV genome and human genome, the codon usage of HPV was almost entirely different from that of humans. Statistical significant of the separation between codons ending with A/U and G/C on the first axis was shown by the principal component analysis. The greater number of the effective number of codon values against the value of GC3s was below the expected values. The correlation between effective number of codon values and both aromaticity and hydrophobicity showed significant high negative correlation. These results showed that composition constraint is likely the key element for codon usage in the HPV genome.
Ключевые слова
Principal component analysis, codon usage., composition constraints, papilloma virus
INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
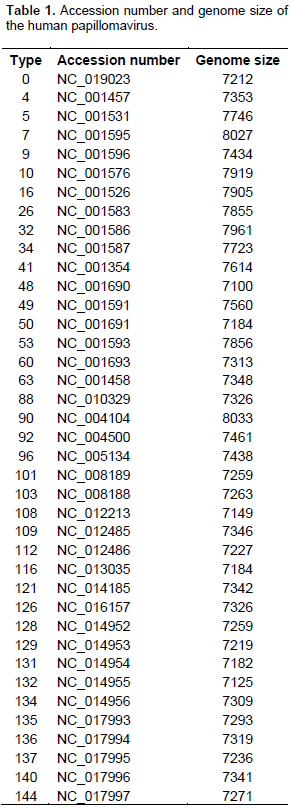
Sequence collection
Relative synonymous codon usage
The principle component analysis
The index of GC3s
The effective number of codon values
Indices of codon preference in the HPV genome
Indices for measuring chemical properties of amino acids
Where, N is the number of amino acids and ki is the hydrophobic index of the ith amino acid.
The aromaticity index (Peden, 1999) is calculated as:
Codon adaptation index
Statistical analysis
Correlation analysis was calculated using Spearman’s rank correlation method of the R package (R Development Core Team, 2011).
RESULTS
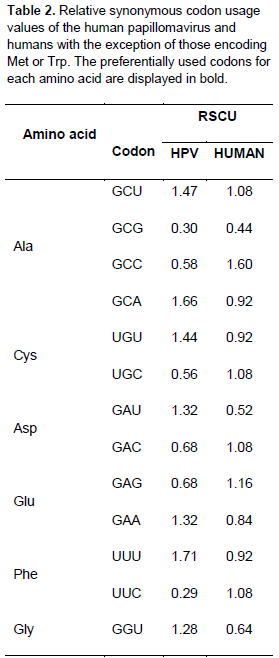
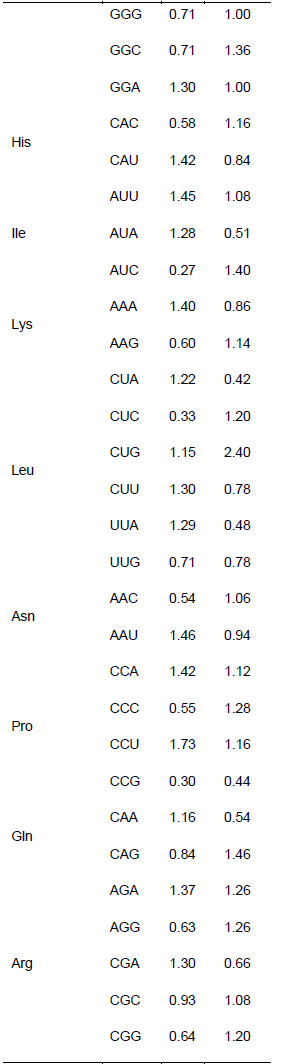
Relative synonymous codon usage of the HPV genome
Overall relative synonymous codon usage of the HPV genome
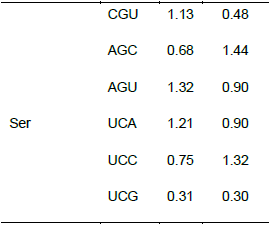
Relationship between the codon usage patterns of HPV and the host
Comparison of the genomes of HPV and humans revealed that the codon usage pattern of the virus was different from that of the host (Figure 1). There were only few similar synonymous codon usage patterns between HPV and humans; these similarities were found in Ala (GGU), Pro (CCA and CCU), Arg (AGA), and Ser (UCU) (Table 2).
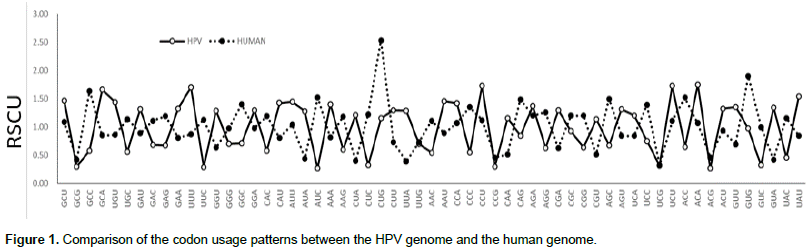
Principle component analysis
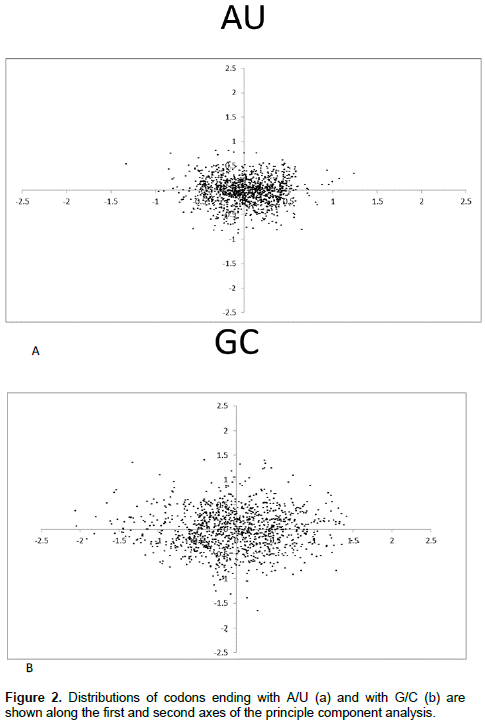
Relationship of ENC values with GC3s
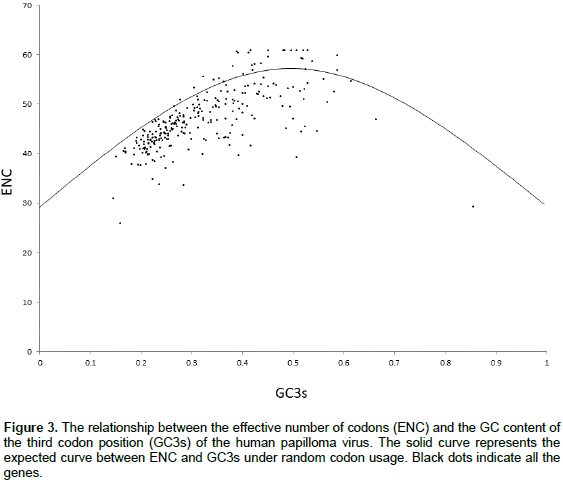
Level of gene expression and codon bias
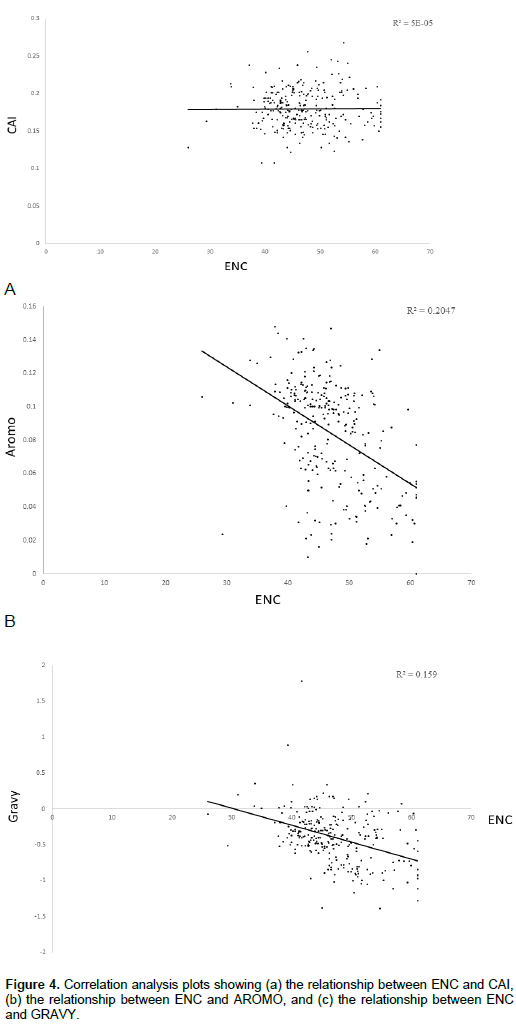
Correlation between ENC and both AROMO and GRAVY
We also investigated whether other factors could explain the codon usage bias seen in the HPV genome. Significant high negative correlation was observed in between ENC and both aromaticity (Figure 4b) (Spearman, r = -0.71464, p < 0.001) and GRAVY (Figure 4c) (Spearman, r = -0.4391, p < 0.001).
DISCUSSION
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
REFERENCES
Bishal AK, Mukherjee R, Chakraborty C (2013). Synonymous codon usage pattern analysis of Hepatitis D virus. Virus Res. 173(2):350-353. | |
Butt AM, Nasrullah I, Tong Y (2014). Genome-wide analysis of codon usage and influencing factors in chikungunya viruses. PLoS One 9(3):e90905. | |
Chen H, Sun S, Norenburg JL, Sundberg P (2014). Mutation and selection cause codon usage and bias in mitochondrial genomes of ribbon worms (Nemertea). PLoS One 9 (1):e85631. | |
Chen Y (2013). A comparison of synonymous codon usage bias patterns in DNA and RNA virus genomes: quantifying the relative importance of mutational pressure and natural selection. Biomed. Res. Int. 406342. | |
Comeron JM, Aguade M (1998). An evaluation of measures of synonymous codon usage bias. J. Mol. Evol. 47(3):268-274. | |
Cristina J, Fajardo A, So-ora M, Moratorio G, Musto H (2016). A detailed comparative analysis of codon usage bias in Zika virus. Virus Res. 223:147-152. | |
Daling JR, Madeleine MM, Johnson LG, Schwartz SM, Shera KA, Wurscher MA, Carter JJ, Porter PL, Galloway DA, McDougall JK (2004). Human papillomavirus, smoking, and sexual practices in the etiology of anal cancer. Cancer 101(2):270-280. | |
Epstein RJ, Lin K, Tan TW (2000). A functional significance for codon third bases. Gene 245(2):291-298. | |
Galloway DA, McDougall JK (1989). Human Papillomaviruses and Carcinomas. Adv. Virus Res. 37:125-171. | |
Grantham R, Gautier C, Gouy M (1980). Codon frequencies in 119 individual genes confirm corsistent choices of degenerate bases according to genome type. Nucleic Acids Res. 8(9):1893-1912. | |
Gu W, Zhou T, Ma J, Sun X, Lu Z (2004). Analysis of synonymous codon usage in SARS Coronavirus and other viruses in the Nidovirales. Virus Res. 101(2):155-161. | |
Gupta SK, Ghosh TC (2001). Gene expressivity is the main factor in dictating the codon usage variation among the genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Gene 273(1):63-70. | |
Heitzer M, Eckert A, Fuhrmann M, Griesbeck C (2007). Influence of Codon Bias on the Expression of Foreign Genes in Microalgae. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 616:46-53. | |
Hu C, Chen J, Ye L, Chen R, Zhang L, Xue X (2014). Codon usage bias in human cytomegalovirus and its biological implication. Gene 545(1):5-14. | |
Jenkins GM, Holmes EC (2003). The extent of codon usage bias in human RNA viruses and its evolutionary origin. Virus Res. 92(1):1-7. | |
Karlin S, Mrázek J (1996). What drives codon choices in human genes? J. Mol. Biol. 262(4):459-472. | |
Lee SY, Cho NH, Choi EC, Baek SJ, Kim WS, Shin DH, Kim SH (2010). Relevance of human papilloma virus (HPV) infection to carcinogenesis of oral tongue cancer. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 39(7):678-683. | |
Liu X, Zhang Y, Fang Y, Wang Y (2012). Patterns and influencing factor of synonymous codon usage in porcine circovirus. Virol. J. 9(1):68. | |
Ma MR, Hui L, Wang ML, Tang Y, Chang YW, Jia QH, Wang XH, Yan W, Ha XQ, Ling H (2014). Overall codon usage pattern of enterovirus 71. Genet. Mol. Res. 13(1):336-343. | |
Mazumder TH, Chakraborty S, Paul P (2014). A cross talk between codon usage bias in human oncogenes. Bioinformation 10(5):973-2063. | |
Nasrullah I, Butt AM, Tahir S, Idrees M, Tong Y (2015). Genomic analysis of codon usage shows influence of mutation pressure, natural selection, and host features on Marburg virus evolution. BMC Evol. Biol. 15:174. | |
Peden FJ (1999). Analysis of codon usage [WWW Document]. PhD Thesis, Univ. Nottingham, UK. URL | |
Peden FJ (2005). CodonW [WWW Document]. 2005. | |
R Development Core Team (2011). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. View | |
RoyChoudhury S, Mukherjee D (2010). A detailed comparative analysis on the overall codon usage pattern in herpesviruses. Virus Res. 148(1-2):31-43. | |
Sablok G, Nayak KC, Vazquez F, Tatarinova TV (2011). Synonymous codon usage, GC (3), and evolutionary patterns across plastomes of three pooid model species: emerging grass genome models for monocots. Mol. Biotechnol. 49(2):116-128. | |
Seedorf K, Krämmer G, Dürst M, Suhai S, Röwekamp WG (1985). Human papillomavirus type 16 DNA sequence. Virology 145(1):181-185. | |
Shackelton LA, Holmes EC (2004). The evolution of large DNA viruses: combining genomic information of viruses and their hosts. Trends Microbiol. 12(10):458-465. | |
Sharp PM, Li WH (1986). Codon usage in regulatory genes in Escherichia coli does not reflect selection for "rare" codons. Nucleic Acids Res. 14(19):7737-7749. | |
Sharp PM, Li WH (1987). The codon adaptation index--a measure of directional synonymous codon usage bias, and its potential applications. Nucleic Acids Res. 15(3):1281-1295. | |
Wright F (1990). The 'effective number of codons'used in a gene. Gene 87(1):23-29. | |
Xia X (2007). An improved implementation of codon adaptation index. Evol. Bioinform. Online 3:53-58. | |
Xu X, Fei D, Han H, Liu H, Zhang J, Zhou Y, Xu C, Wang H, Cao H, Zhang H (2017). Comparative characterization analysis of synonymous codon usage bias in classical swine fever virus. Microb. Pathog. 107:368-371. | |
Zhang Y, Liu Y, Liu W, Zhou J, Chen H, Wang Y, Ma L, Ding Y, Zhang J (2011). Analysis of synonymous codon usage in hepatitis A virus. Virol. J. 8:174. | |
Zhang Z, Dai W, Wang Y, Lu C, Fan H (2013). Analysis of synonymous codon usage patterns in torque teno sus virus 1 (TTSuV1). Arch. Virol. 158(1):145-154. | |
Zhao KN, Chen J (2011). Codon usage roles in human papillomavirus. Rev. Med. Virol. 21(6):397-411. | |
Zhao KN, Liu WJ, Frazer IH (2003). Codon usage bias and A+T content variation in human papillomavirus genomes. Virus Res. 98(2):95-104. | |
Zheng ZM, Baker CC (2006). Papillomavirus genome structure, expression, and post-transcriptional regulation. Front. Biosci. 11:2286-2302. | |
Zhong Q, Xu W, Wu Y, Xu H (2012). Patterns of synonymous codon usage on human metapneumovirus and its influencing factors. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 460837. | |
Zhou J, Liu WJ, Peng SW, Sun XY, Frazer I (1999). Papillomavirus capsid protein expression level depends on the match between codon usage and tRNA availability. J. Virol. 73(6):4972-4982. | |